Data Governance Overview
Aligning with Wright State University's Strategic Plan 2030, data governance establishes a structured approach to data management, safeguards data assets and promotes data quality, integrity, and accessibility.
Benefits
- Improves institutional efficiency.
- Encourages collaboration, data literacy, and trust in the responsible handling of data.
- Provides the foundation for shared institutional data definitions, business analytics and reporting, and business process guides.
Framework
Data governance establishes a framework for managing data as a strategic institutional asset. It ensures that data is accurate, consistent, secure, and appropriately used to support decision-making at every level. Effective data governance is sustained by people who take ownership and accountability, processes that provide structure and guidance, and technology that enables efficiency and reliability.
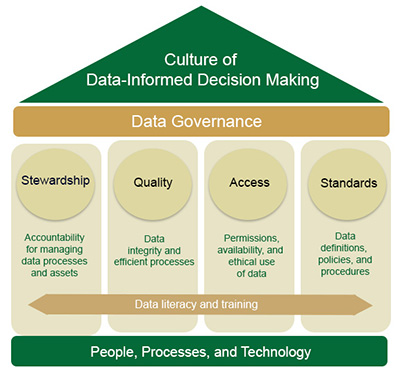
This framework is built on the foundational pillars of stewardship, quality, access, and standards. Each pillar is strengthened through data literacy and training. Together, these elements create a culture of data-informed decision-making that advances institutional goals and supports student success.
- Stewardship assigns responsibility for managing data and related processes. Stewards act as custodians, ensuring that data is accurate, used appropriately, and protected.
- Quality ensures data is accurate, reliable, consistent, and relevant for its intended purposes. Maintaining high-quality data supports trustworthy reporting, sound decision-making, and efficient operations.
- Access is the process of retrieving and using data in a secure and responsible way. It supports effective decision-making and system use while balancing availability with requirements for privacy, compliance, and security.
- Standards establish policies, definitions, formats, and classifications to ensure data remains consistent across systems. They enable data to be shared, understood, and applied effectively throughout the institution.
Roles & Responsibilities
Executive Committee
Individual members of the President’s Cabinet who provide program oversight, high-level project approval and prioritization, policy approval, and project funding.
Data Governance Council
Council Members ensure and support the effective management of data assets and project portfolios of the University by establishing procedures and standards, making policy recommendations, advocating for appropriate resources, and guiding and monitoring data governance efforts.
Data Trustees
University officials with responsibility over institutional data and processes as designated by the Data Governance Council. Data trustees are accountable for managing, protecting, and ensuring the integrity and usefulness of institutional data and for upholding Wright State University policies, state laws, and federal laws applicable to the institutional data and the processes that support them.
Data stewards
University staff who help define, implement, and oversee data management policies and procedures within their specific data domain. Institutional data stewards have delegated responsibility for all aspects of how data is acquired, used, stored and protected throughout the full data life cycle from acquisition through disposition.
Data Domains & Access
Data domains are high-level categories of institutional data/processes, as designated by the Data Governance Council.